Pomeranian Voivodeship
| Pomeranian Voivodeship Województwo pomorskie |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| — Voivodeship — | |||
|
|||
.png) |
|||
| Coordinates (Gdańsk): | |||
| Country | |||
| Capital | Gdańsk | ||
| Counties |
4 cities, 16 land counties *
|
||
| Area | |||
| - Total | 18,293 km2 (7,063 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2006) | |||
| - Total | 2,201,069 | ||
| - Density | 120.3/km2 (311.6/sq mi) | ||
| - Urban | 1,478,802 | ||
| - Rural | 722,267 | ||
| Car plates | G | ||
| Website | http://www.woj-pomorskie.pl | ||
| * further divided into 123 gminas | |||


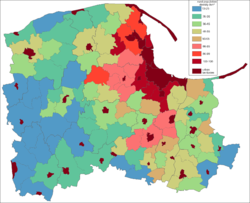
Pomeranian Voivodeship, known in Polish as województwo pomorskie [vɔjɛˈvut͡stfɔ pɔˈmɔrskʲɛ] or simply Pomorskie, is a voivodeship, or province, in north-central Poland. It comprises most of Pomerelia (the most easterly part of historical Pomerania), as well as an area east of the Vistula river. The western part of the province, around Słupsk, belonged historically to Farther Pomerania, while Pomerelia and the eastern bank of the Vistula belonged to the historical region of Prussia. The central parts of the province are also known as Kashubia, named after the Kashubian minority. The provincial capital is Gdańsk.
The voivodeship was established on January 1, 1999, out of the former voivodeships of Gdańsk, Elbląg and Słupsk, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998. It is bordered by West Pomeranian Voivodeship to the west, Greater Poland and Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeships to the south, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship to the east, and the Baltic Sea to the north. It also shares a short land border with Russia, on the Vistula Spit.
Gdańsk, the regional capital, forms part of the Tricity of Sopot, Gdańsk and Gdynia. The voivodeship also includes the narrow Hel Peninsula and the Polish half of the Vistula Spit. Other tourist destinations include Sopot, Jurata, Łeba, Władysławowo, Puck, Krynica Morska, Ustka, Jastarnia, Rozewie, Kuźnica, and many fishing ports and lighthouses.
Most of the territory of the voivodeship was until 1918 part of Germany’s West Prussia, which had the same city – then Danzig – as its capital.
Contents |
Cities and towns
The voivodeship contains 42 cities and towns. These are listed below in descending order of population (according to official figures for 2006[1] ):
|
|
Administrative division
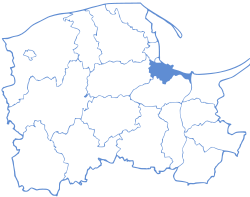
Gdański
Pomeranian Voivodeship is divided into 20 counties (powiats): 4 city counties and 16 land counties. These are further divided into 123 gminas.
The counties are listed in the following table (ordering within categories is by decreasing population).
| English and Polish names |
Area (km²) |
Population (2006) |
Seat | Other towns | Total gminas |
| City counties | |||||
| Gdańsk | 262 | 457,630 | 1 | ||
| Gdynia | 136 | 252,443 | 1 | ||
| Słupsk | 43.15 | 98,402 | 1 | ||
| Sopot | 17.31 | 39,836 | 1 | ||
| Land counties | |||||
| Wejherowo County powiat wejherowski |
1,280 | 181,834 | Wejherowo | Rumia, Reda | 10 |
| Starogard County powiat starogardzki |
1,345 | 121,963 | Starogard Gdański | Skarszewy, Skórcz, Czarna Woda | 13 |
| Tczew County powiat tczewski |
698 | 112,614 | Tczew | Pelplin, Gniew | 6 |
| Kartuzy County powiat kartuski |
1,120 | 109,311 | Kartuzy | Żukowo | 8 |
| Słupsk County powiat słupski |
2,304 | 92,172 | Słupsk * | Ustka, Kępice | 10 |
| Chojnice County powiat chojnicki |
1,364 | 91,585 | Chojnice | Czersk, Brusy | 5 |
| Gdańsk County powiat gdański |
793 | 85,566 | Pruszcz Gdański | 8 | |
| Kwidzyn County powiat kwidzyński |
835 | 80,704 | Kwidzyn | Prabuty | 6 |
| Bytów County powiat bytowski |
2,193 | 75,313 | Bytów | Miastko | 10 |
| Puck County powiat pucki |
578 | 74,196 | Puck | Władysławowo, Jastarnia, Hel | 7 |
| Kościerzyna County powiat kościerski |
1,166 | 66,778 | Kościerzyna | 8 | |
| Lębork County powiat lęborski |
707 | 63,659 | Lębork | Łeba | 5 |
| Malbork County powiat malborski |
495 | 62,960 | Malbork | Nowy Staw | 6 |
| Człuchów County powiat człuchowski |
1,574 | 56,797 | Człuchów | Czarne, Debrzno | 7 |
| Sztum County powiat sztumski |
731 | 41,808 | Sztum | Dzierzgoń | 5 |
| Nowy Dwór Gdański County powiat nowodworski (pomorski) |
653 | 35,498 | Nowy Dwór Gdański | Krynica Morska | 5 |
| * seat not part of the county | |||||
Economy
Major corporations
| Corporation name Further information |
Location | Kind of activity |
| Energa Gdańsk Power Generator [1] | Gdańsk | energy supplies |
| Ergo Hestia [2] | Sopot | insurance |
| Gdańsk Repair Yard[3] | Gdańsk | repair shipyard |
| Gdynia Stocznia [4] | Gdynia | shipyard |
| GE Capital Bank[5] | Gdańsk | banking |
| Grupa LOTOS [6] | Gdańsk | petroleum products |
| Intel Technology Poland [7] | Gdańsk | hardware |
| International Paper Kwidzyn [8] | Kwidzyn | paper products |
| Lubiana [9] | Łubiana near Kościerzyna | china-ware manufacturer |
| Philips Consumer Electronics | Kwidzyn | electronics |
| Polpharma[10] | Starogard Gdański | medicines |
| Prokom Software [11] | Gdynia | software |
| Destylarnia Sobieski [12] | Starogard Gdański | distillery |
| Elnord [13] | Gdańsk | energy supplies |
| LPP [14] | Gdańsk | designing and distributing clothes |
| Source:[2] | ||
Unemployment

Transport
- SKM
- Gdańsk Lech Wałęsa Airport
- Obwodnica Trójmiejska
- Autostrada A1
Education

Higher education
| Name | Location | Students in thousands |
|
| total | of which women |
||
| Total | - | 97.9 | 55.3 |
| Uniwersytet Gdański (Gdańsk University) |
Tricity | 29.3 | 19.4 |
| Politechnika Gdańska (Gdańsk University of Technology) |
Gdańsk | 17.6 | 5.9 |
| Akademia Pomorska w Słupsku (Pomeranian Academy in Słupsk) |
Słupsk | 8.1 | 6.0 |
| Akademia Medyczna w Gdańsku (Medical University of Gdańsk) |
Gdańsk | 4.2 | 3.1 |
| Akademia Wychowanie Fizycznego i Sportu w Gdańsku (Sports Academy in Gdańsk) |
Gdańsk | 4.1 | 1.9 |
| Akademia Sztuk Pięknych w Gdańsku (Arts Academy in Gdańsk) |
Gdańsk | 0.9 | 0.7 |
| Akademia Marynarki Wojennej im. Bohaterów Westerplatte (Polish Naval Academy) |
Gdynia | . | . |
| Akademia Morska w Gdyni (Gdynia Maritime University) |
Gdynia | . | . |
| Gdańskie Seminarium Duchowne (Gdańsk Seminary) |
Gdańsk | . | . |
| Akademia Muzyczna im. Stanisława Moniuszki w Gdańsku (The Stanisław Moniuszko Academy of Music in Gdańsk) |
Gdańsk | . | . |
| Data as of 31 November 2005, source http://www.stat.gov.pl | |||
Protected areas

Protected areas in Pomeranian Voivodeship include two National Parks and nine Landscape Parks. These are listed below.
- Słowiński National Park (a UNESCO-designated biosphere reserve)
- Tuchola Forest National Park
- Coastal Landscape Park
- Iława Lake District Landscape Park (partly in Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship)
- Kashubian Landscape Park
- Słupia Valley Landscape Park
- Tricity Landscape Park
- Tuchola Landscape Park (partly in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship)
- Vistula Spit Landscape Park
- Wdydze Landscape Park
- Zaborski Landscape Park
Most popular surnames in the region
- Wiśniewski: 7,446
- Kamiński: 6,752
- Lewandowski: 6,687
Previous Pomeranian Voivodeships
Pomeranian Voivodeship (1294–1308)
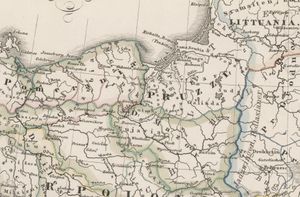
Pomeranian Voivodeship was a province of the Kingdom of Poland. After the extinction of the local dukes in 1294, the province fell to Przemysł II of Poland.
Pomeranian Voivodeship (1466–1772)

This was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Kingdom of Poland from 1454/1466 until the partitions in 1772/1795. Together with the Chełmno Voivodeship and Malbork Voivodeship it formed the historical province of Royal Prussia. The capital was at Gdańsk. It was renamed to the Prussian province of West Prussia (1772–1919).
Voivodeship Governor (Wojewoda) seat:
Regional council (sejmik generalny)
- Gniew
Regional councils (sejmik poselski i deputacki)
- Człuchów
- Tuchola
- Świecie
- Starogród
- Puck
Administrative divisions:
- Człuchów County, (Powiat Człuchowski), Człuchów
- Gdańsk County, (Powiat Gdański), Gdańsk
- Koscierzyna County, (Powiat Kościerzyński), Kościerzyna
- Mirachowo County, (Powiat Mirachowski), Mirachowo
- Nowe County, (Powiat Nowski), Nowe
- Puck County, (Powiat Pucki), Puck
- Skarszewy County, (Powiat Skarszewski), Skarszewy
- Starogard County, (Powiat Starogrodzki) Starogard Gdański
- Świecie County, (Powiat Świecki), Świecie
- Tczew County, (Powiat Tczewski), Tczew
- Tuchola County, (Powiat Tucholski), Tuchola
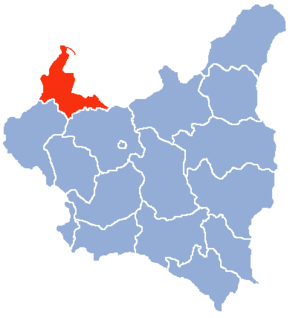
Pomeranian Voivodeship (1919–1939)
This was a unit of administration and local government in the Republic of Poland (II Rzeczpospolita) established in 1919 after World War I from the majority of the Prussian province of West Prussia which fell to Poland. Toruń was the capital. In 1938–1939 the voivodeship extended to the south at the expense of Poznań Voivodeship and Warsaw Voivodeship, and was called Great Pomerania afterwards (see: Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on April 1, 1938).
During WWII it was occupied by Nazi Germany and annexed as Reichsgau Danzig-Westpreussen "(Reich province of Gdańsk-West Prussia)." In 1945 it was returned to Poland and superseded by Gdańsk and Bydgoszcz voivodeships. In the years 1975–1998 it was reorganized into the voivodeships of Gdańsk, Elbląg, Bydgoszcz, Toruń and Włocławek.
Pomeranian Voivodeship (1945–1950)
This was a unit of administration and local government in Poland established in 1945 from most of the pre-war Pomeranian Voivodeship, later renamed Bydgoszcz Voivodeship.
Capital city: Bydgoszcz
List of counties in 1946
English county name, Polish county name, capital city
- Bydgoszcz City, miasto Bydgoszcz
- Toruń City, miasto Toruń
- Brodnica County, powiat brodnicki, Brodnica
- Bydgoszcz County, powiat bydgoski, Bydgoszcz
- Chełmno County, powiat chełmiński, Chełmno
- Chojnice County, powiat chojnicki, Chojnice
- Grudziądz County, powiat grudziądzki, Grudziądz
- Inowrocław County, powiat inowroclawski, Inowrocław
- Lipno County, powiat lipnowski/lipnieński?, Lipno
- Lubawa County, powiat lubawski, Lubawa
- Nieszawa County, powiat nieszawski, Nieszawa
- Rypin County, powiat rypiński, Rypin
- Sępolno County, powiat sępoleński, Sępolno Krajenskie
- Świecie County, powiat świecki, Świecie
- Szubin County, powiat szubiński, Szubin
- Toruń County, powiat toruński, Toruń
- Tuchola County, powiat tucholski, Tuchola
- Wąbrzeźno County, powiat wąbrzeski, Wąbrzeźno
- Włocławek County, powiat włocławski, Włocławek
- Wyrzysk County, powiat wyrzyski, Wyrzysk
References
External links
- Information about Pomeranian Voivodeship - official website (en)
- Economy brochure (en)
- The Pomorskie Voivodeship. The Greatest Tourist Attractions - Brochure (en)
- Pomerania Development Agency Co. (en)
- Wrota Pomorza - Pomeranian Voivodeship Portal (en) (de) (fr) (pl) (ru)
|
||||||||||
|
|||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

